Oscillating Systems
Oscillating Systems: Overview
We will study the oscillating systems in this topic. We will also go through various types of oscillations. Moreover, we will discuss the characteristics of different oscillatory motions through some graphs.
Important Questions on Oscillating Systems
Calculate the time period of a simple pendulum of length on the surface of the moon. The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is the acceleration due to gravity on earth.{ }
A pendulum clock gives correct time at and at a place where .It is taken to a hill where the acceleration of gravity is
At what temperature will it give correct time? Coefficient of linear expansion of steel =
How much time a clock will gain or lose when taken from a place at to a place having the temperature ?
. The coefficient of cubical expansion of iron=
A mass is suspended with a weightless spring. When the spring is slightly pulled and released then the mass oscillates with the time period . If the mass is increased by , then the time period becomes . Determine the ratio .
A mass is suspended one by one by two springs of force constants . The time periods of their oscillations are respectively. If the same mass be suspended by connecting the two springs in parallel then the time period of oscillations is .The correct relation is:
Derive an expression for the time period of two loaded springs in parallel combination.
Find an expression for the time period of a vertical spring-mass system.
What will be the effect on the time period of a pendulum using a copper wire, if it has been taken to a room where the temperature is higher by .
Discuss the effect of temperature on the time period of simple pendulum.
What is percentage change in the time period, if the length of the simple pendulum increases by ?
According to the law of the simple pendulum . Does it mean that when ? explain.
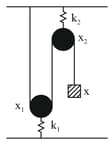
The time period for small vertical oscillations of a block of mass when the masses of the pulleys are negligible and spring constant and is
A light spring of force constant is cut into two equal halves and the two are connected in parallel; the equivalent force constant of the system is
A light spring of constant is cut into two equal parts. The spring constant of each part is
In a spring-mass system, the length of the spring is , and it has a mass attached to it and oscillates with an angular frequency . The spring is then cut into two parts, one (a) with relaxed length and the other (b) with relaxed length . The force constants of the two springs and are
In case of a simple pendulum, time period versus length is depicted by
A simple pendulum of length has mass and oscillates freely with amplitude of . Its potential energy at extreme position is
A simple pendulum with a bob of mass and charge makes oscillations in seconds. A vertical electric field of magnitude pointing downward is applied. The time taken by the pendulum to make oscillations in the electric field is (Acceleration due to gravity )
